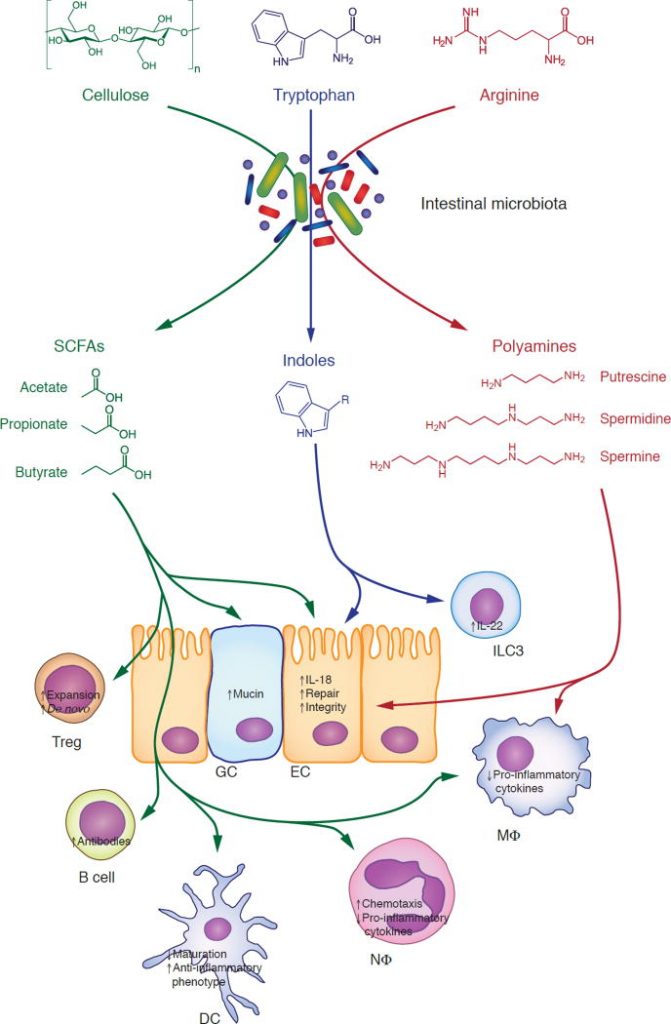
The human gastrointestinal tract is populated by a various, extremely mutualistic microbial flora, which is called the microbiome.
Disruptions to the microbiome have been proven to be related to extreme pathologies of the host, together with metabolic illness, most cancers, and inflammatory bowel illness. Mood and habits are additionally inclined to alterations in the intestine microbiota.
A very placing instance of the symbiotic results of the microbiome is the immune system, whose cells rely critically on a various array of microbial metabolites for regular growth and habits.
This contains metabolites which are produced by micro organism from dietary parts, metabolites which are produced by the host and biochemically modified by intestine micro organism, and metabolites which are synthesized de novo by intestine microbes.
In this overview, we spotlight the function of the intestinal microbiome in human metabolic and inflammatory ailments and focus specifically on the molecular mechanisms that govern the gut-immune axis.
A cross-sectional examine on dental surgeons’ immune standing towards hepatitis B virus in the Public Health System.
Hepatitis B is a extreme public well being downside. The foremost world well being facilities have mentioned it because of its pandemic proportion, excessive pathogenicity and infectivity.
This examine aimed to find out the immunization profile of dental surgeons – towards hepatitis B virus (HBV) in the Public Health System (PHS) via the detection of anti-HBsAg antibodies by immunochromatography and associations with dental surgeons’ social and instructional profile, components associated to skilled data and practices.
This is a cross-sectional examine on the prevalence of vaccination and immune standing to HBV in dentists of Sao Paulo State PHS.
Data assortment occurred in three levels: questionnaire software, evaluation of adhesion to the vaccination protocol and anti-HBsAg checks.
Statistical evaluation used the Bivariate Analysis and the Binary Logistic Regression. From the complete of 219 interviewees, 74.9% reported having acquired three doses of the vaccine, however 35.6% weren’t resistant to HBV.
The dependent variable was related to years in the public service (years) (OR [Odds Ratio]=1.04; 95% CI 1.00-1.08); data on the topic (OR=6.93; 95% CI 1.39-34.40); incorrect reply regarding the etiological agent of the illness (OR=2.60; 95% CI 1.30-5.22); ignorance on the variety of vaccine doses which were administered (OR=3.43; 95% CI 1.14-10.30); and lower than three doses of the vaccine in the immunization schedule (OR=8.76; 95% CI 3.50-21.91).
A substantial portion of execs non-immune to the HBV have been discovered. We concluded that data, years of apply and completion of the vaccination schedule (three doses) affected dental surgeons’ immune standing to HBV.